- Spring 2023
NCAT Completes Second Mixture Performance Testing Round Robin
In 2021, NCAT conducted a second Round Robin evaluation to include several mixture performance tests being evaluated for balanced mix design (BMD) implementation and quality assurance (QA) during production. The objective is to help participating labs benchmark their results and generate data to develop within-lab and between-lab variability estimates of the different test procedures. NCAT reached out to State DOTs, contractors, consulting firms, and materials suppliers to learn what tests would be of interest for this second Round Robin evaluation. Participating labs selected the tests they wanted to perform. The most popular tests in the evaluation are:
- Hamburg Wheel Tracking Test [HWTT] (AASHTO T 324-19),
- Asphalt Pavement Analyzer [APA] (AASHTO T 340-10),
- IDEAL Cracking Test or IDEAL-CT (ASTM 8225-19),
- High-temperature Indirect Tensile Strength Test (HT-IDT), and
- Indirect Tensile Asphalt Rutting Test [IDEAL-RT] (ASTM D8360-22).
The HT-IDT and IDEAL-RT are two relatively new rutting tests that are gaining popularity for QA evaluation; because they are simple, quick, repeatable, and correlate well with the traditional wheel-tracking rutting tests (i.e., HWTT and APA). Both tests can be conducted in a Marshall-style press and are similar. The IDEAL-RT uses a shear fixture instead of an indirect tension fixture, as shown in Figure 1. The HWTT, APA, and IDEAL-CT were all previously evaluated in the 2018 NCAT Round Robin.
For the evaluation, a single plant mix produced for an experiment on the 2021 NCAT Test Track is used. This mixture was designed using the BMD process. The mixture is a 12.5 mm NMAS mix containing a PG 64-22 binder and 20% RAP. Participating labs received enough plant mix to fabricate specimens for their selected tests. NCAT provided the participating labs with detailed instructions on specimen fabrication and testing along with data files to report the results.
NCAT screened the data for the Round Robin evaluation for quality prior to incorporation into the database. The database was then used to determine the within-lab and between-lab coefficients of variation (CV) of the tests per ASTM E691-19 “Standard Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method”. As noted in the 2018 Round Robin evaluation, ASTM E691-19 recommends between three to six materials to be included to develop full precision statements. Although this evaluation only included one mixture, the data is still useful to provide preliminary estimates of test variability.
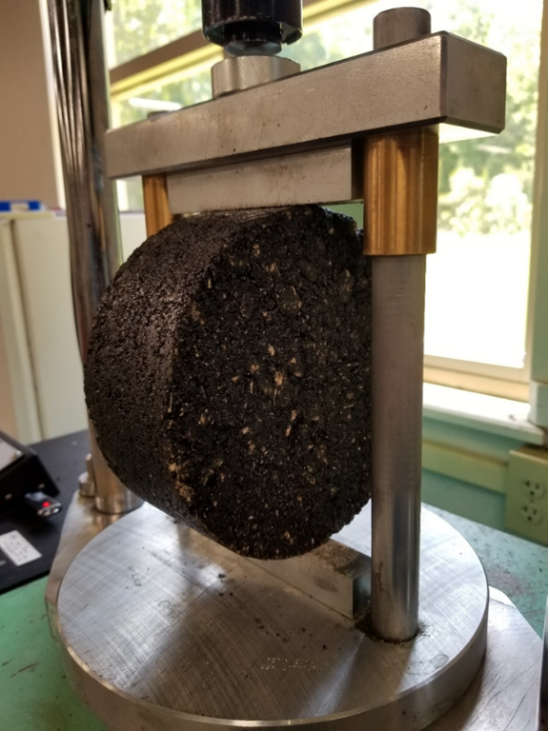
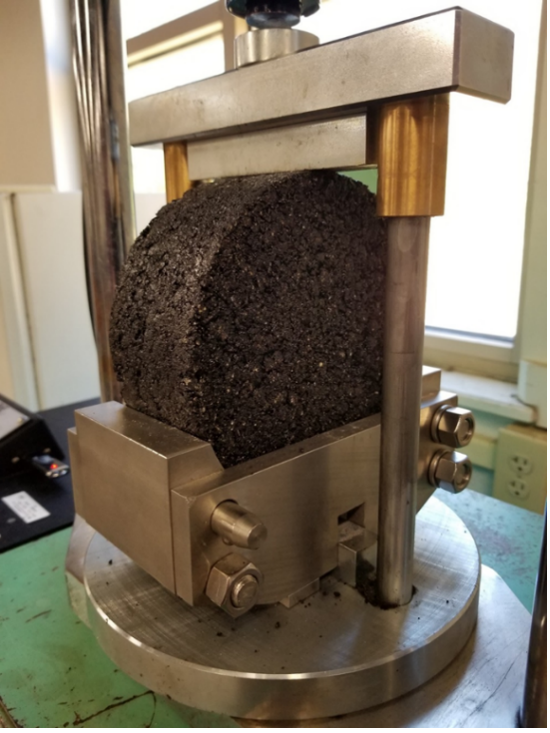


Figure 1: HT-IDT Test Setup (left) and IDEAL-RT Test Setup (right).
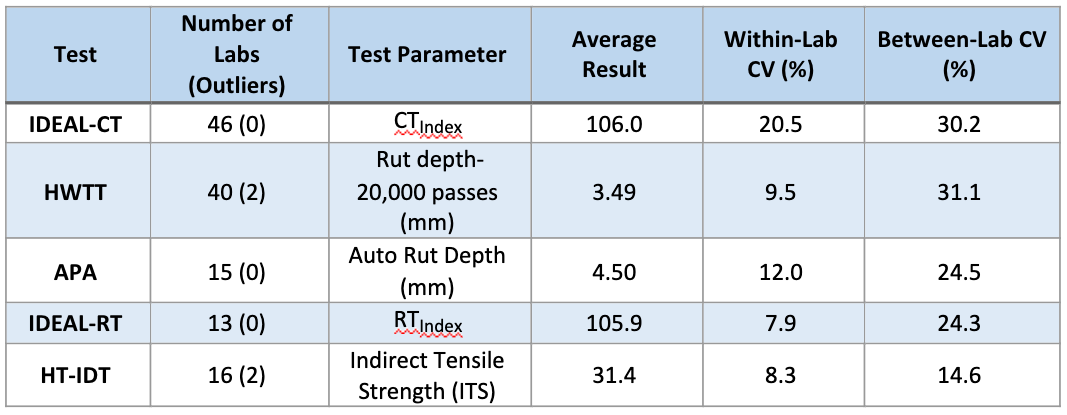
The within-lab and between-lab variability estimates for this second Round Robin are summarized in Table 1. The main findings from this evaluation are as follows:
- IDEAL-CT was conducted at 25°C. Forty-six (46) labs were included in the evaluation and no labs were identified as outliers. The average CTIndex was 106.0, with a within-lab CV of 20.5%, and a between-lab CV of 30.2%. When compared to the results of the 2018 evaluation, the within-lab CV are consistent for both studies at around 20%. The between-lab CV for the 2022 study is 5% lower compared to the 2018 study. This is likely due to triple the number of labs participating in the 2022 study relative to the 2018 study.
- HWTT was conducted at 50°C and the variability was assessed for rut depths at 20,000-wheel passes. Forty (40) labs were included in the analysis, with two labs deemed as outliers and removed from the analysis. The average rut depth at 20,000 passes was 3.49 mm, with a within-lab CV of 9.5% and a between-lab CV of 31.1%. When compared to the results of the 2018 study, the within-lab CV was around 10% for both studies. The between-lab CV showed a 5% increase when compared to the 2018 results. Since the mixtures and the participating labs for both studies were different, this may have contributed to the difference in the between-lab variability between the two Round Robin studies.
- APA test was conducted at 64°C. The analysis included fifteen (15) labs with no outlier labs removed from the analysis. The average rut depth was 4.5 mm with a within-lab CV, and between-lab CV of 12.0% and 24.5%, respectively. Both the within-lab and between-lab variations obtained for this study were lower than those reported in the 2018 study. This may be attributable to an increase in the number of participating labs in the 2022 study.
- IDEAL-RT was conducted at 50°C. Thirteen (13) labs were included in the evaluation with no outlier labs identified. The average RTIndex was 105.9 with a within-lab CV of 7.9% and between-lab CV of 24.3%.
- HT-IDT was also conducted at 50°C with eighteen (18) labs included in the evaluation. Two labs were identified as outliers and removed from the analysis. The results yielded an average ITS of 31.4 psi with a within-lab CV of 8.3% and between-lab CV of 14.6%. From all the rutting tests evaluated in the second Round Robin, the HT-IDT yielded the lowest between-lab variability.
Table 1: ASTM E 691-19 Precision Estimates Second NCAT Round Robin Study.
NCAT’s goal is to conduct similar Round Robin studies every couple of years to support the asphalt industry with their BMD implementation effort, which will result in improved pavement performance.



Contact Carolina Rodezno (left), Adam Taylor (middle), or Nathan Moore (right) for more information about this research.